3.8 KiB
3.8 KiB
E6A Semiconductor materials and devices: semiconductor materials; bipolar junction transistors; operation and types of field-effect transistors
- E6A01 (C) In what application is gallium arsenide used as a semiconductor material? #card
- E6A02 (A) Which of the following semiconductor materials contains excess free electrons? #card
- E6A03 (C)
Why does a PN-junction diode not conduct current when reverse biased? #card
- A. Only P-type semiconductor material can conduct current
- B. Only N-type semiconductor material can conduct current
- C. Holes in P-type material and electrons in the N-type material are separated by the applied voltage, widening the depletion region
- D. Excess holes in P-type material combine with the electrons in N-type material, converting the entire diode into an insulator
- E6A04 (C) What is the name given to an impurity atom that adds holes to a semiconductor crystal structure? #card
- E6A05 (C) How does DC input impedance at the gate of a field-effect transistor (FET) compare with that of a bipolar transistor? #card
- E6A06 (B) What is the beta of a bipolar junction transistor? #card
- E6A07 (D) Which of the following indicates that a silicon NPN junction transistor is biased on? #card
- E6A08 (D) What is the term for the frequency at which the grounded-base current gain of a bipolar junction transistor has decreased to 0.7 of the gain obtainable at 1 kHz? #card
- E6A09 (A)
What is a depletion-mode field-effect transistor (FET)? #card
- A. An FET that exhibits a current flow between source and drain when no gate voltage is applied
- B. An FET that has no current flow between source and drain when no gate voltage is applied
- C. An FET that exhibits very high electron mobility due to a lack of holes in the N-type material
- D. An FET for which holes are the majority carriers
- E6A10 (B)
In Figure E6-1, which is the schematic symbol for an N-channel dual-gate MOSFET? #card
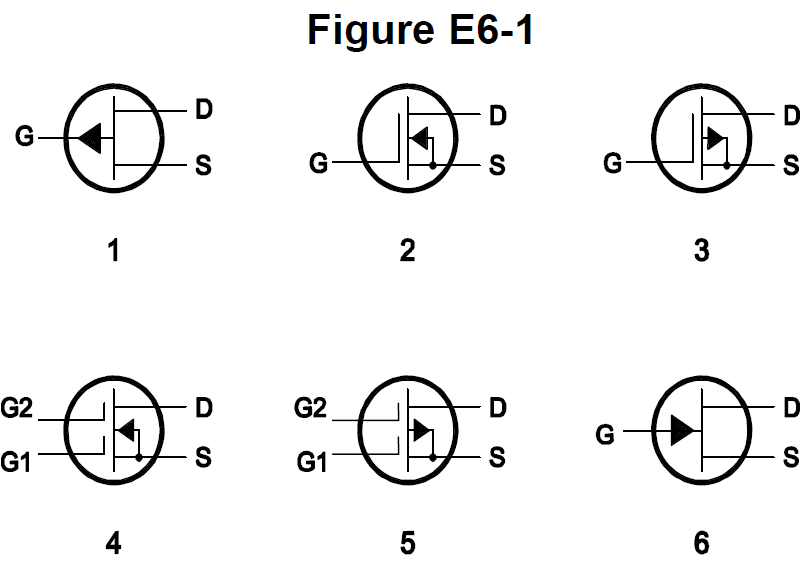
- E6A11 (A)
In Figure E6-1, which is the schematic symbol for a P-channel junction FET? #card

- E6A12 (D) What is the purpose of connecting Zener diodes between a MOSFET gate and its source or drain? #card