4.9 KiB
4.9 KiB
E7D Power supplies and voltage regulators; solar array charge controllers
- E7D01 (D) How does a linear electronic voltage regulator work? #card
- E7D02 (B) How does a switchmode voltage regulator work? #card
- E7D03 (A) What device is used as a stable voltage reference? #card
- E7D04 (B) Which of the following describes a three-terminal voltage regulator? #card
- E7D05 (D) Which of the following types of linear voltage regulator operates by loading the unregulated voltage source? #card
- E7D06 (C)
What is the purpose of Q1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-2? #card
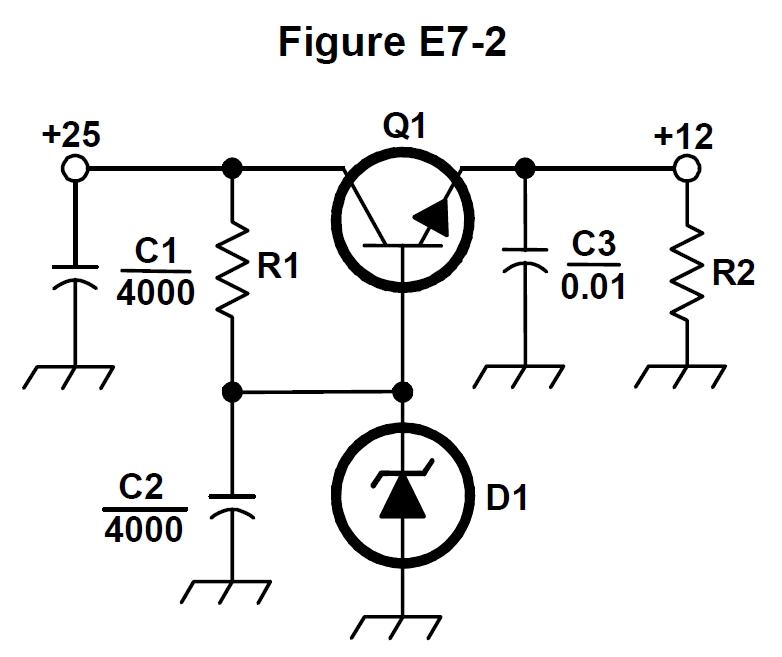
- E7D07 (A)
What is the purpose of C2 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-2? #card
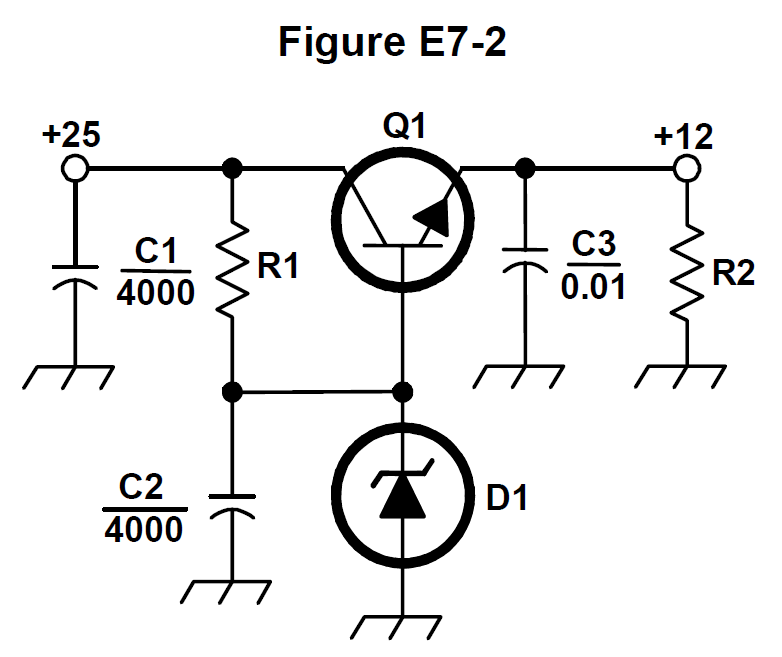
- E7D08 (C)
What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-2? #card
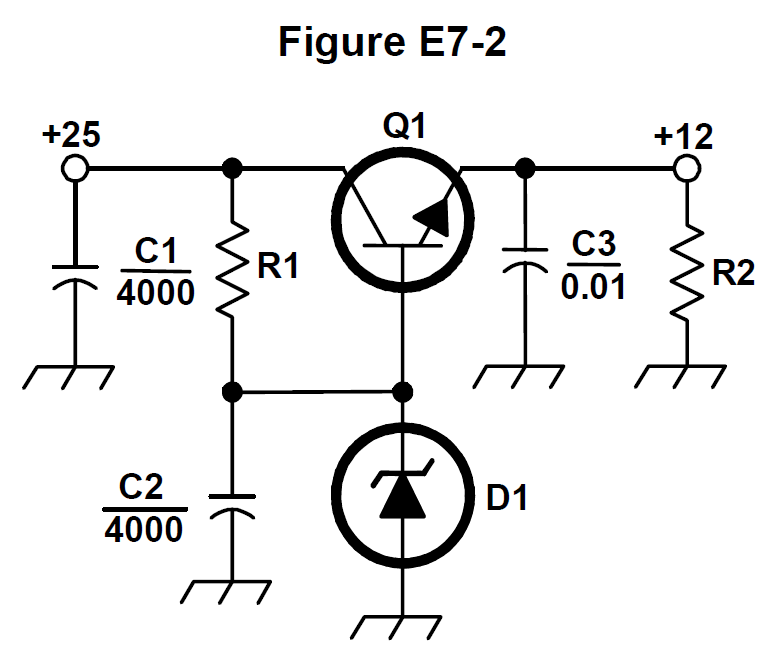
- E7D09 (C) How is battery operating time calculated? #card
- E7D10 (C)
Why is a switching type power supply less expensive and lighter than an equivalent linear power supply? #card
- A. The inverter design does not require an output filter circuit
- B. The control circuitry uses less current, therefore smaller heat sinks are required
- C. The high frequency inverter design uses much smaller transformers and filter components for an equivalent power output
- D. It recovers power from the unused portion of the AC cycle, thus using fewer components
- E7D11 (D) What is the purpose of an inverter connected to a solar panel output? #card
- E7D12 (C) What is the dropout voltage of a linear voltage regulator? #card
- E7D13 (C) Which of the following calculates power dissipated by a series linear voltage regulator? #card
- E7D14 (D) What is the purpose of connecting equal-value resistors across power supply filter capacitors connected in series? #card
- E7D15 (D) What is the purpose of a step-start circuit in a high-voltage power supply? #card