3.7 KiB
3.7 KiB
E7B Amplifiers: class of operation; vacuum tube and solid-state circuits; distortion and intermodulation; spurious and parasitic suppression; switching-type amplifiers
- E7B01 (A) For what portion of the signal cycle does each active element in a push-pull, Class AB amplifier conduct? #card
- E7B02 (A) What is a Class D amplifier? #card
- E7B03 (A) What circuit is required at the output of an RF switching amplifier? #card
- E7B04 (A) What is the operating point of a Class A common emitter amplifier? #card
- E7B05 (C) What can be done to prevent unwanted oscillations in an RF power amplifier? #card
- E7B06 (B) What is a characteristic of a grounded-grid amplifier? #card
- E7B07 (D) Which of the following is the likely result of using a Class C amplifier to amplify a single-sideband phone signal? #card
- E7B08 (B) Why are switching amplifiers more efficient than linear amplifiers? #card
- E7B09 (D) What is characteristic of an emitter follower (or common collector) amplifier? #card
- E7B10 (B)
In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R1 and R2? #card
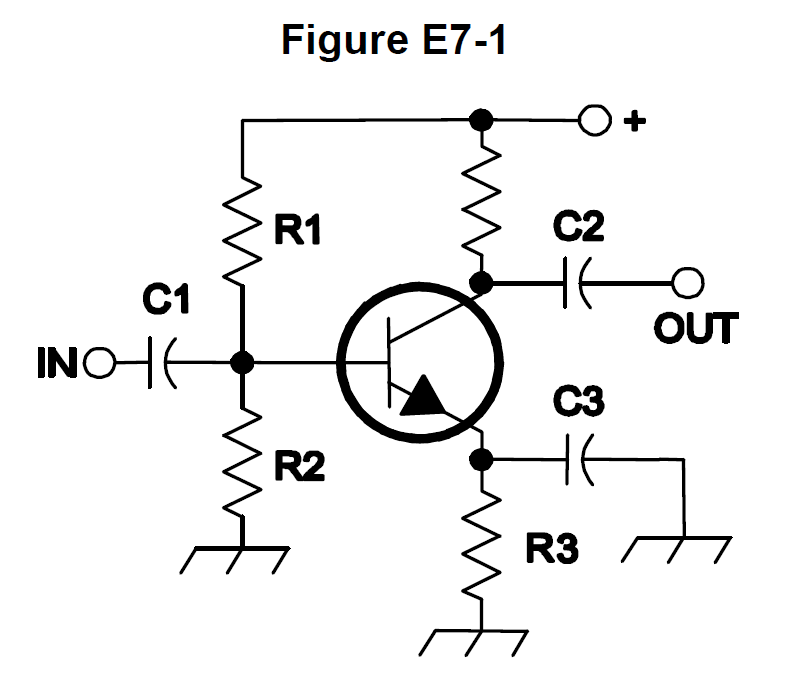
-
E7B11 (D) In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R3? #card

- E7B12 (C)
What type of amplifier circuit is shown in Figure E7-1? #card
