3.1 KiB
3.1 KiB
E6C Digital ICs: families of digital ICs; gates; programmable logic devices
- E6C01 (A) What is the function of hysteresis in a comparator? #card
- E6C02 (B) What happens when the level of a comparator’s input signal crosses the threshold voltage? #card
- E6C03 (A) What is tri-state logic? #card
- E6C04 (C) Which of the following is an advantage of BiCMOS logic? #card
- E6C05 (D) Which of the following digital logic families has the lowest power consumption? #card
- E6C06 (C) Why do CMOS digital integrated circuits have high immunity to noise on the input signal or power supply? #card
- E6C07 (B)
What best describes a pull-up or pull-down resistor? #card
- A. A resistor in a keying circuit used to reduce key clicks
- B. A resistor connected to the positive or negative supply used to establish a voltage when an input or output is an open circuit
- C. A resistor that ensures that an oscillator frequency does not drift
- D. A resistor connected to an op-amp output that prevents signals from exceeding the power supply voltage
- E6C08 (B)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for a NAND gate? #card
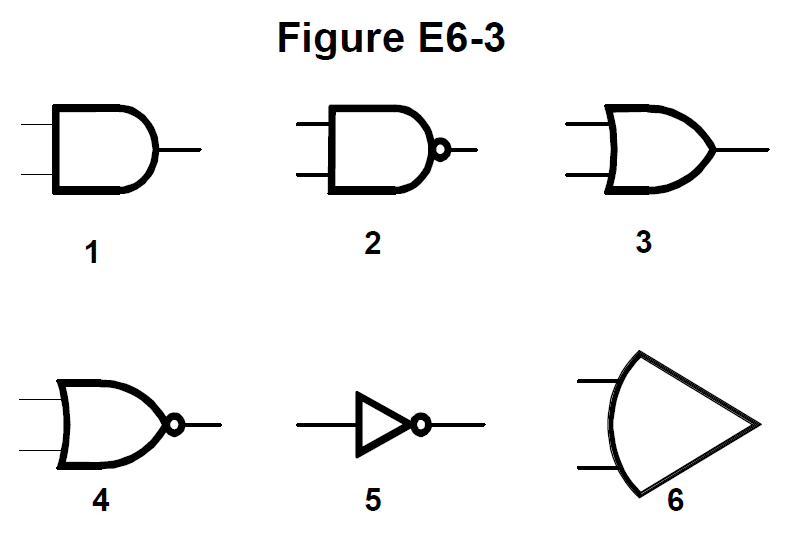
- E6C09 (B) What is used to design the configuration of a field-programmable gate array (FPGA)? #card
- E6C10 (D)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for a NOR gate? #card

- E6C11 (C)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for the NOT operation (inversion)? #card
