E6B Diodes
- E6B01 (B)
What is the most useful characteristic of a Zener diode? #card
- A. A constant current drop under conditions of varying voltage
- B. A constant voltage drop under conditions of varying current
- C. A negative resistance region
- D. An internal capacitance that varies with the applied voltage
- E6B02 (D)
Which characteristic of a Schottky diode makes it a better choice than a silicon junction diode for use as a power supply rectifier? #card
- A. Much higher reverse voltage breakdown
- B. More constant reverse avalanche voltage
- C. Longer carrier retention time
- D. Lower forward voltage drop
- E6B03 (B)
What property of an LED's semiconductor material determines its forward voltage drop? #card
- A. Intrinsic resistance
- B. Band gap
- C. Junction capacitance
- D. Junction depth
- E6B04 (A)
What type of semiconductor device is designed for use as a voltage-controlled capacitor? #card
- A. Varactor diode
- B. Tunnel diode
- C. Silicon-controlled rectifier
- D. Zener diode
- E6B05 (D)
What characteristic of a PIN diode makes it useful as an RF switch? #card
- A. Extremely high reverse breakdown voltage
- B. Ability to dissipate large amounts of power
- C. Reverse bias controls its forward voltage drop
- D. Low junction capacitance
- E6B06 (D)
Which of the following is a common use of a Schottky diode? #card
- A. In oscillator circuits as the negative resistance element
- B. As a variable capacitance in an automatic frequency control circuit
- C. In power supplies as a constant voltage reference
- D. As a VHF/UHF mixer or detector
- E6B07 (B)
What causes a junction diode to fail from excessive current? #card
- A. Excessive inverse voltage
- B. Excessive junction temperature
- C. Insufficient forward voltage
- D. Charge carrier depletion
- E6B08 (A)
Which of the following is a Schottky barrier diode? #card
- A. Metal-semiconductor junction
- B. Electrolytic rectifier
- C. PIN junction
- D. Thermionic emission diode
- E6B09 (C)
What is a common use for point-contact diodes? #card
- A. As a constant current source
- B. As a constant voltage source
- C. As an RF detector
- D. As a high-voltage rectifier
- E6B10 (B)
In Figure E6-2, which is the schematic symbol for a Schottky diode? #card
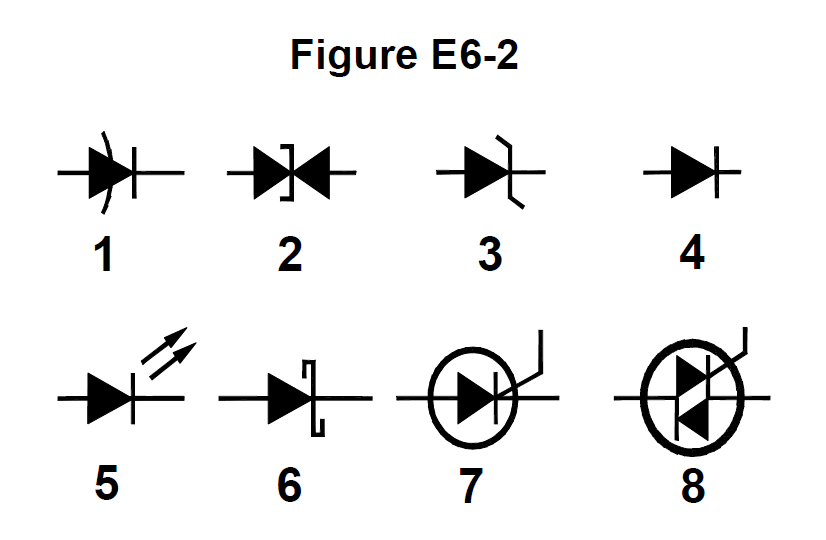
- E6B11 (A)
What is used to control the attenuation of RF signals by a PIN diode? #card
- A. Forward DC bias current
- B. A variable RF reference voltage
- C. Reverse voltage larger than the RF signal
- D. Capacitance of an RF coupling capacitor
